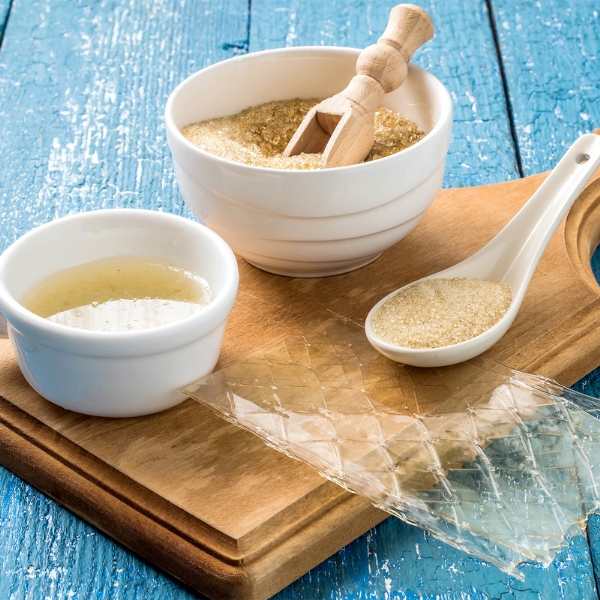
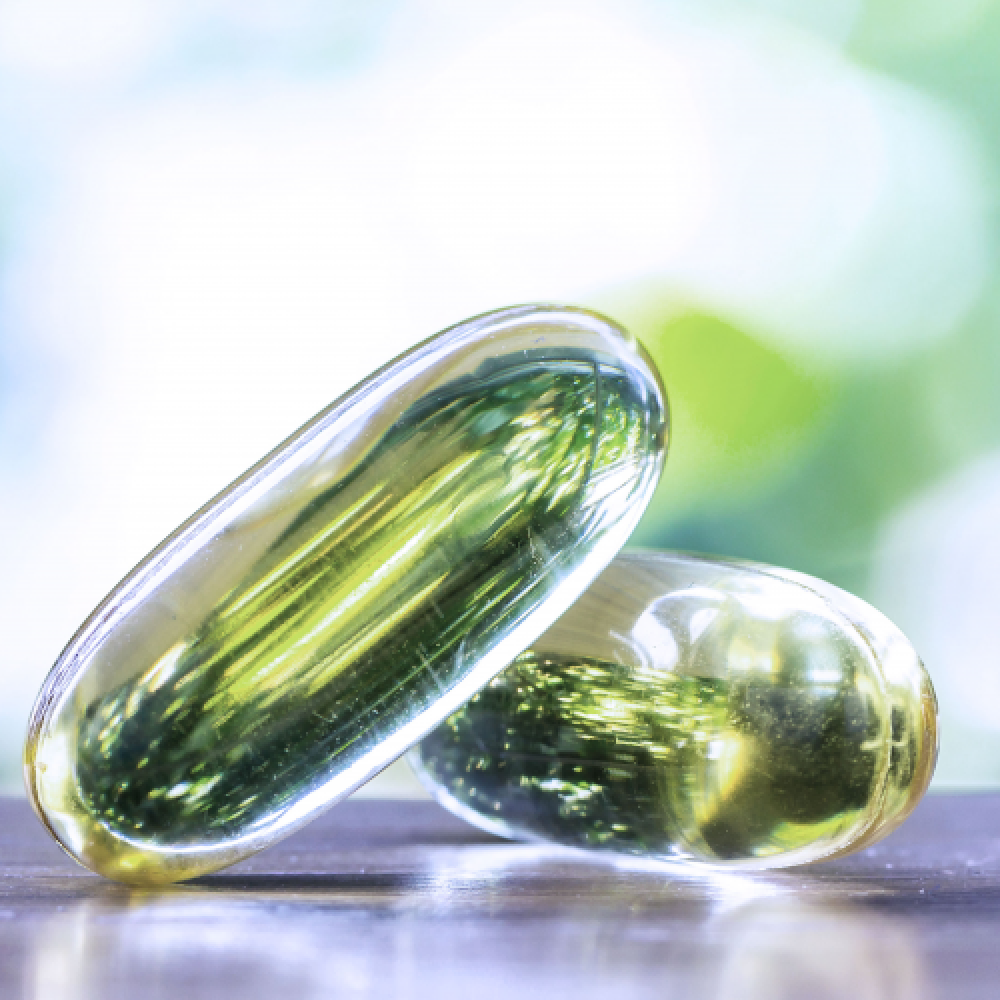
By sourcing premium animal skin from halal-certified suppliers, we guarantee a superior gelatin product that meets customer expectations for quality, purity, and ethical production practices, while also adhering to the highest standards of halal compliance.
Exceptional Quality Features:
- Our gelatin boasts an exceptional bloom strength, ensuring excellent gelling properties and texture.
- We guarantee a low ash content, resulting in a clearer and more transparent gel.
- Our gelatin is free from contaminants and impurities, ensuring a consistent quality in every batch.
- Our gelatin meets the highest standards of halal and kosher certification, making it suitable for global consumption.
- We produce gelatin that meets the stringent requirements of both food and pharmaceutical industries.